Introduction
Technology has become an indispensable tool in the research and conservation of Arctic wolves. From GPS tracking and drones to camera traps and satellite imagery, various technological advancements are providing scientists with new ways to study and protect this elusive species
This article explores the critical role of technology in Arctic wolf research, the advancements and challenges faced in conservation efforts, and the potential future technologies that could further aid in the preservation of these majestic creatures
The Role of Technology in Arctic Wolf Research
The integration of technology in Arctic wolf research has significantly enhanced our understanding of these elusive animals. By employing various technological tools, researchers can gather more accurate and comprehensive data, which is crucial for the conservation and management of Arctic wolf populations
GPS Tracking and Arctic Wolves
GPS tracking has revolutionized the way scientists monitor Arctic wolves. By fitting wolves with GPS collars, researchers can track their movements in real-time. This technology provides invaluable data on the wolves’ range, migration patterns, and hunting behaviors
For example, a study conducted by the University of Minnesota used GPS collars to track the movement patterns of Arctic wolves, revealing that they travel an average of 12 miles per day during the hunting season. This data helps in understanding the wolves’ territorial needs and the impact of environmental changes on their behavior
GPS collars are designed to withstand the harsh Arctic conditions, ensuring continuous data collection over extended periods. The information gathered from these collars is transmitted to researchers via satellites, allowing for remote monitoring without disturbing the animals
This non-invasive approach is crucial for studying the natural behaviors of Arctic wolves in their habitat
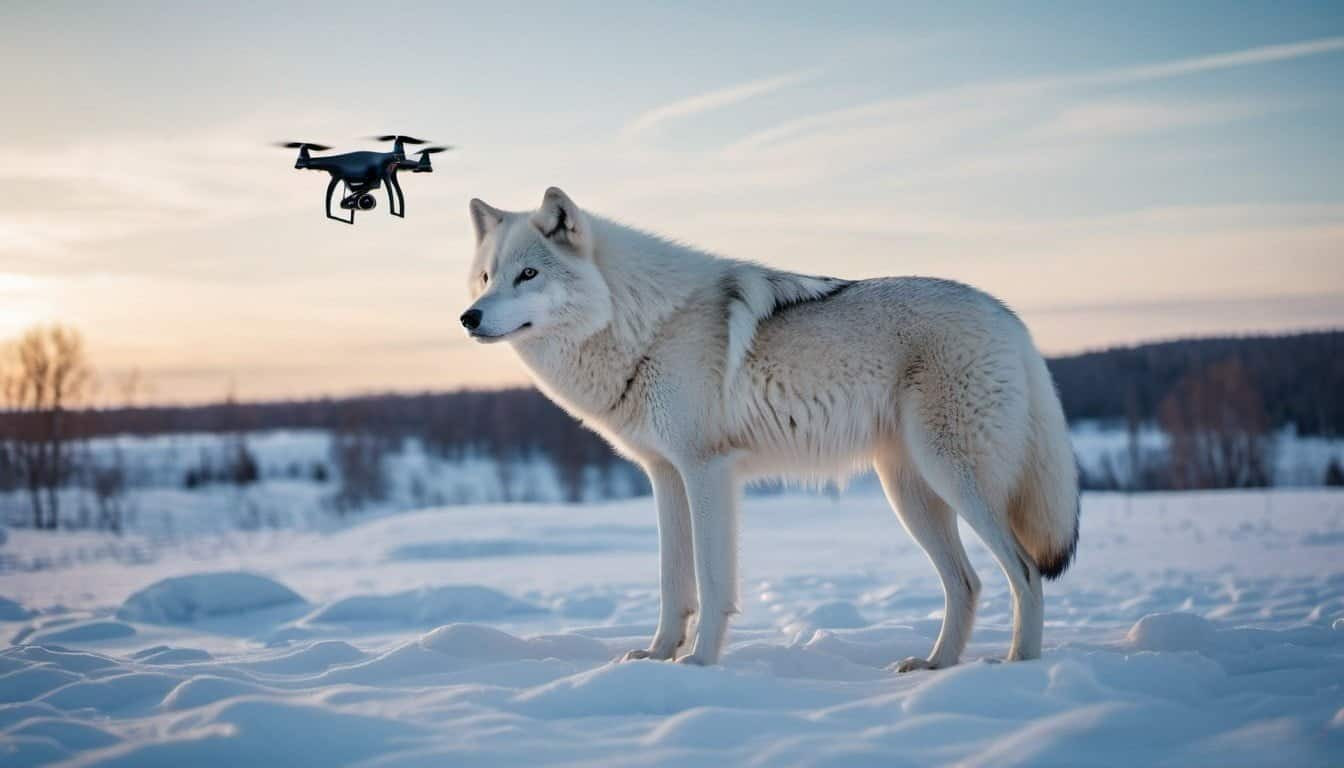
Drones in Monitoring Wolf Populations
Drones have become an essential tool in wildlife research, including the study of Arctic wolves. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) provide a bird’s-eye view of the landscape, allowing researchers to conduct aerial surveys and monitor wolf populations without physically traversing the harsh Arctic terrain
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras can capture detailed images and videos, helping scientists identify individual wolves, track pack movements, and observe hunting behaviors
A study published in the journal “Remote Sensing in Ecology and Conservation” demonstrated the effectiveness of drones in monitoring Arctic wolf populations
The researchers used drones to survey a remote area in northern Canada, identifying 11 distinct wolf packs and documenting their activities over several months. This technology not only enhances the efficiency of population monitoring but also reduces the risk and cost associated with traditional ground surveys
Camera Traps for Behavioral Studies
Camera traps are another vital technology used in Arctic wolf research. These motion-activated cameras are strategically placed in the wolves’ habitat to capture images and videos of their activities
Camera traps provide insights into the wolves’ behavior, social structure, and interactions with other wildlife. By analyzing the footage, researchers can study the wolves’ hunting strategies, denning behaviors, and pack dynamics
A project led by the Wildlife Conservation Society utilized camera traps to study the behavior of Arctic wolves in Greenland. The footage revealed rare insights into the wolves’ social interactions, including grooming, play, and territorial marking. This information is essential for understanding the social structure of wolf packs and developing effective conservation strategies
Camera traps also offer the advantage of continuous monitoring over long periods, allowing researchers to gather data even in the absence of field personnel. This passive data collection method minimizes human interference and provides a more accurate representation of the wolves’ natural behaviors
Technological Advancements and Challenges in Arctic Wolf Conservation
The integration of cutting-edge technologies has brought significant advancements in the conservation efforts of Arctic wolves. These tools have provided researchers with more detailed data and new methods for studying and protecting these animals
However, the use of technology also comes with its own set of challenges
Satellite Imagery for Habitat Analysis
Satellite imagery has become an invaluable resource for understanding and conserving Arctic wolf habitats
By using high-resolution images from satellites, researchers can analyze the landscape, track changes in habitat, and identify critical areas for wolf survival. This data is essential for assessing the impact of climate change and human activities on Arctic ecosystems
A study conducted by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) utilized satellite imagery to monitor changes in Arctic wolf habitats over the past two decades. The study found significant shifts in vegetation patterns and the availability of prey, directly affecting wolf populations
Satellite imagery allows for large-scale habitat analysis, providing a comprehensive view of the environmental factors influencing Arctic wolves
Software Tools for Data Analysis
The vast amount of data collected through GPS collars, drones, and camera traps requires sophisticated software tools for analysis
These tools help researchers process and interpret the data, making it easier to identify patterns and trends. Software programs like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are particularly useful for mapping wolf movements and habitat use
For example, the Wildlife Research Institute uses GIS software to analyze the spatial data collected from GPS collars. This analysis helps in understanding the wolves’ territorial ranges and identifying critical corridors for their movement
Advanced statistical software also aids in analyzing behavioral data from camera traps, providing insights into social structures and interactions within wolf packs
Overcoming Challenges in Tech-Based Research
While technology offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that researchers must overcome. One significant issue is the harsh Arctic environment, which can interfere with the functionality of technological devices. Extreme temperatures, snow, and ice can damage equipment, leading to data loss or inaccuracies
Another challenge is the high cost associated with deploying and maintaining advanced technologies in remote Arctic regions. GPS collars, drones, and satellite imagery require significant financial investment, which can be a limiting factor for many research projects
Additionally, the logistical challenges of reaching and operating in remote areas can further complicate the use of technology
To address these challenges, researchers are continuously working on developing more robust and cost-effective solutions. Innovations such as solar-powered GPS collars and drones with extended battery life are helping to mitigate some of the environmental and financial constraints
Collaborations between research institutions, conservation organizations, and technology companies are also crucial in advancing the use of technology in Arctic wolf conservation
Future Technologies and Collaboration in Arctic Wolf Conservation
As technology continues to advance, new tools and methods are emerging that promise to further enhance Arctic wolf research and conservation efforts
These innovations, coupled with increased collaboration between technologists and conservationists, hold the potential to significantly improve the protection and understanding of Arctic wolves
Emerging Technologies on the Horizon
Several emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize the study and conservation of Arctic wolves. One such technology is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms. These tools can analyze large datasets more efficiently and accurately than traditional methods, identifying patterns and trends that might be missed by human researchers
For instance, AI can be used to process images and videos captured by drones and camera traps, automatically identifying individual wolves and their behaviors
This automation reduces the time and labor required for data analysis, allowing researchers to focus on developing conservation strategies. Additionally, advancements in DNA analysis and genetic mapping offer new insights into the genetic diversity and health of Arctic wolf populations, aiding in the development of targeted conservation plans
Potential Impacts of New Tech on Conservation Efforts
The introduction of new technologies can have a profound impact on the effectiveness of conservation efforts. Enhanced tracking and monitoring tools provide more accurate data on wolf populations and their habitats, enabling better-informed management decisions
For example, integrating real-time GPS data with predictive modeling can help anticipate and mitigate potential threats to wolf populations, such as habitat loss or changes in prey availability due to climate change
Moreover, the use of advanced imaging technologies, such as thermal cameras and multispectral sensors, allows for the detection of wolves and other wildlife in challenging conditions, such as during the polar night or through dense vegetation. These tools improve the ability to conduct year-round monitoring and ensure that conservation measures are timely and responsive to the wolves’ needs
Collaboration Between Technologists and Conservationists
Effective collaboration between technologists and conservationists is crucial for maximizing the benefits of new technologies in Arctic wolf conservation. By working together, these experts can develop and implement innovative solutions tailored to the specific challenges of studying and protecting Arctic wolves
Collaborative projects, such as those funded by government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private companies, can pool resources and expertise to address complex conservation issues
For example, partnerships between universities and technology firms have led to the development of more durable and efficient tracking devices designed specifically for the harsh Arctic environment. These collaborations also foster the exchange of knowledge and skills, ensuring that conservationists are well-equipped to use new technologies effectively
In addition, engaging local communities in conservation efforts and integrating traditional ecological knowledge with modern technology can enhance the overall success of these initiatives. Indigenous peoples often have valuable insights into the behavior and ecology of Arctic wolves, and their involvement can lead to more culturally sensitive and sustainable conservation practices
Conclusion
The role of technology in the research and conservation of Arctic wolves is indispensable and continuously evolving. Advanced tools such as GPS tracking, drones, and camera traps have provided researchers with unprecedented insights into the behavior and ecology of these elusive animals
These technologies enable scientists to monitor wolf movements, study their social structures, and understand their interactions with the environment with greater accuracy and less intrusion
Technological advancements have also significantly improved habitat analysis and data interpretation. Satellite imagery and sophisticated software tools help identify critical areas for wolf survival and assess the impacts of environmental changes
However, the harsh Arctic conditions and high costs associated with these technologies pose significant challenges that researchers must address through innovation and collaboration
Looking ahead, emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and genetic mapping offer promising new avenues for Arctic wolf conservation. The integration of these cutting-edge tools can enhance data analysis, improve monitoring capabilities, and lead to more effective conservation strategies
Successful conservation efforts will depend on the collaboration between technologists, conservationists, and local communities, combining modern innovations with traditional knowledge to protect and preserve Arctic wolf populations for future generations